Recombination and Recombination Rate
Recently, I read the Adam Auton’s PhD Thesis “The Estimation of Recombination Rates from Population Genetic Data”, this blog is its notes.
Recombination
Homologous recombination is the process by which a pair of homologous DNA sequences exchange some portion of their DNA. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be passed on from the parents to the offspring
The recombination was found by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1911, when studying the chromosome theory of heredity. And his student Sturtevant uses crossover data to construct the first genetic map in drosophila. Read more here.
A model for the process by which recombination occurs in eukaryotes was proposed in 1964 by Robin Holliday (HOLLIDAY 1964). It shows two possible resolutions, known as Gene Conversion and Crossover. When talking about recombination, people always mean crossover as it leaves a much larger singal easy to trace.

Recombination Rate (centimorgan, cM)
A commonly used unit of recombination rate is the centimorgan, which is defined as a 1% chance that two loci will be separated by a recombination event in one generation.
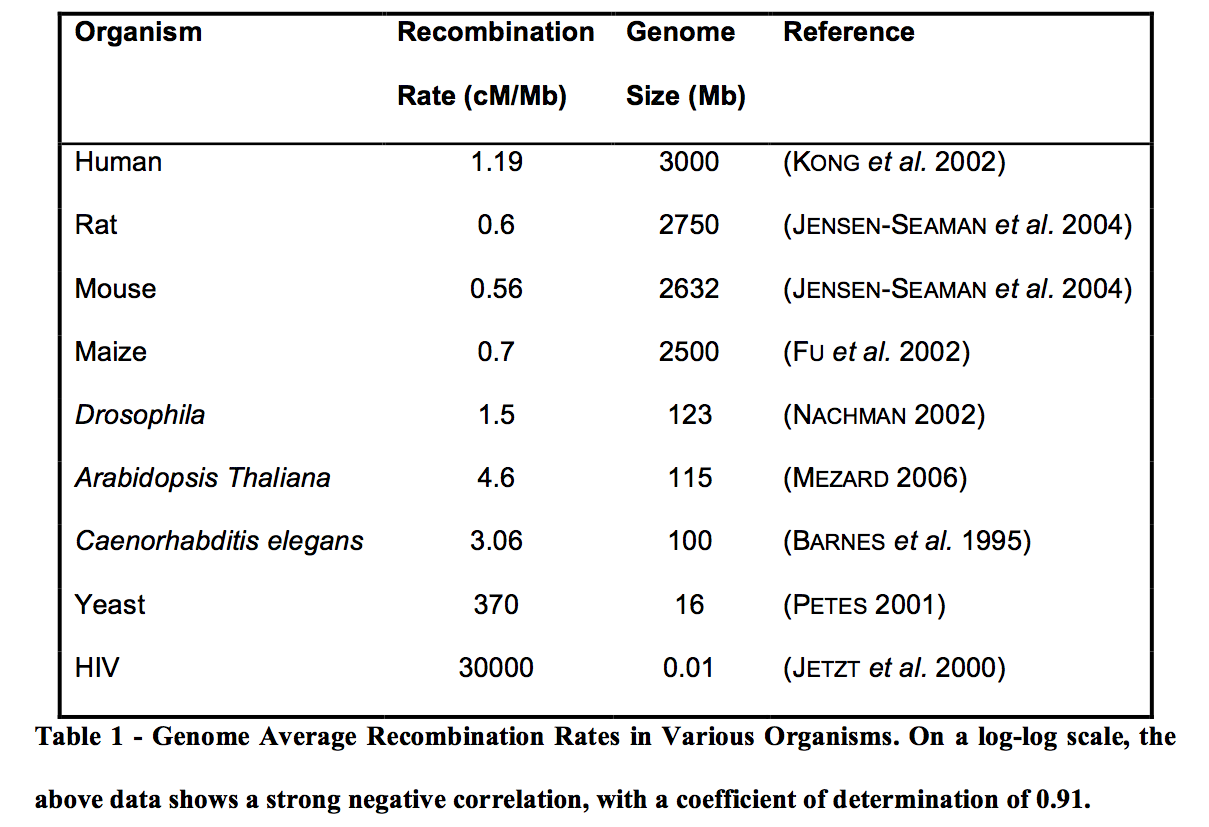
In eukaryotes, there is a notable uniformity in the total recombination map length regardless of genome size (AWADALLA 2003). The average recombination rate is therefore negatively correlated with genome size.
Recombination Rate Estimation
There are some methods to estimate the reombination rate.
Genotyping a large number of individuals in families
In 2002, deCODE company (KONG et al. 2002) constructed a map from a large pedigree study of 869 individuals in 146 Icelandic families. They found
- The shorter chromosomes tended to have higher recombination rates than the larger chromosomes
- There was also a high degree of rate heterogeneity within chromosomes
- an average of 1.65 times longer in females than in males
Sperm Typing
Sperm typing is to search for recombination sequences in the sperm product of male individuals.
MHC Region
A 216kb region of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6 has been extensively studied by sperm typing (JEFFREYS et al. 2001)
The rate of recombination in these regions could be hundred or thousands of times that of the surrounding regions, and hence these areas were dubbed recombination hotspots.
Population data
Recombination information can also be seem in the population genetic data.
Recombination events break down the amout of LD between loci. However, it is unclear how such statistics can be directly related to the underlying recombination rate (DEVLIN and RISCH 1995).
One early and simple method is known as four-gamete test (WEIR 1979). But it has very low power.
Nowadays, people, such as 23andme, use population data, such as HapMap to estimate the recombination rate using more complicated model and algorithms.
The genetic map provide by IMPUTE
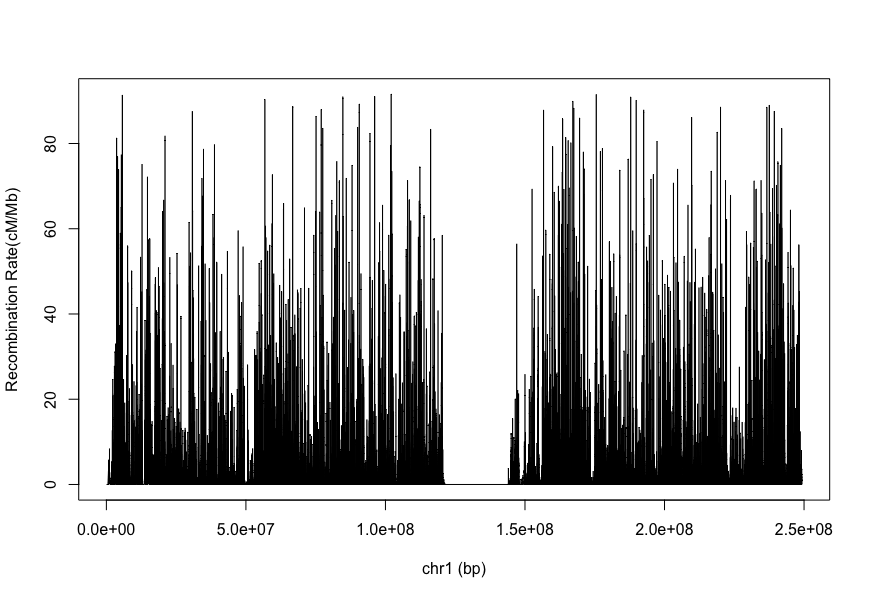
The imputation software IMPUTE2 provide the genetic map for human in its website.
We can have use its data to a look the recombination across the human genome.
library(data.table)
data = fread("genetic_map_chr1_combined_b37.txt")
plot(data$"position",data$"COMBINED_rate(cM/Mb)",type="l", xlab="chr1 (bp)", ylab="Recombination Rate(cM/Mb)")