软件测试简介
注:内容引用和翻译自Paul Ammann和Jeff Offutt的书《Introduction to Software Testing》。
测试工程师的工作
A test engineer is an information technology (IT) professional who is in charge of one or more technical test activities, including designing test inputs, producing test case values, running test scripts, analyzing results, and reporting results to developers and managers.
- 测试工程师:负责一个或者多个测试工作的IT专业人员。
- 测试工程师的工作:设计测试输入(test inputs),给出测试用例结果(test case values),运行测试脚本,分析测试结果,并向开发和经理进行汇报。
A test manager is in charge of one or more test engineers. Test managers set test policies and processes, interact with other managers on the project, and otherwise help the engineers do their work.
- 测试经理:负责一个或者多个测试工程师。
- 测试经理的工作:设定测试规则和流程,与项目的其他经理交流,帮助测试工程师工作的进行。
测试分类 - 基于软件
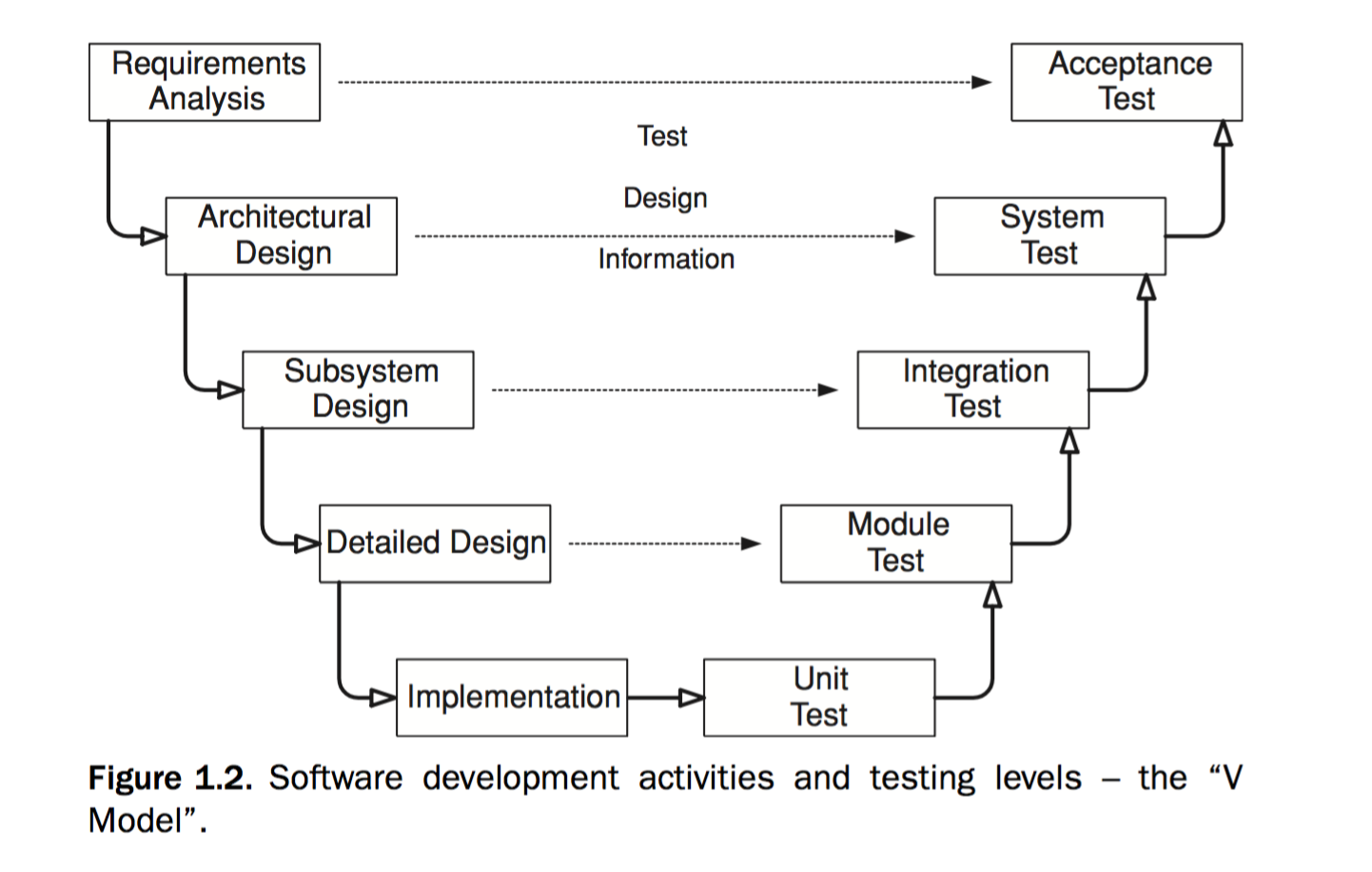
验收测试(Acceptance Test) - 需求分析(requirements analysis)
The requirements analysis phase of software development captures the customer’s needs. Acceptance testing is designed to determine whether the completed software in fact meets these needs. In other words, acceptance testing probes whether the software does what the users want. Acceptance testing must involve users or other individuals who have strong domain knowledge.
- 软件开发的需求分析阶段需要掌握用户的需求。
- 验收测试就是用来检验完成的软件是否真正地满足了用户的这些需求。即验收测试用来探究软件所做的是否是用户想要的。
- 验收测试必须有用户或者有很强相关领域背景知识的人参与。
系统测试(System Test) - 架构设计(Architectural Design)
The architectural design phase of software development chooses components and connectors that together realize a system whose specification is intended to meet the previously identified requirements. System testing is designed to determine whether the assembled system meets its specifications. It assumes that the pieces work individually, and asks if the system works as a whole. This level of testing usually looks for design and specification problems. It is a very expensive place to find lower-level faults and is usually not done by the programmers, but by a separate testing team.
- 软件开发的架构设计阶段需要选择用于实现满足客户需求的系统的组件和连接器(components and connectors)
- 系统测试用来检验搭建的系统是否满足要求。我们会假设系统的每一块都都可以独立工作,然后去确定整个系统作为一个整体是否正常工作。
- 这个阶段的测试经常可以发现设计和要求上的问题。在这个阶段发现底层错误(lower-level faults)是非常昂贵的。系统测试经常不由开发人员进行,而是一个独立的测试团队。
集成测试(Integration Test) - 子系统设计(Subsystem Design)
The subsystem design phase of software development specifies the structure and behavior of subsystems, each of which is intended to satisfy some function in the overall architecture. Often, the subsystems are adaptations of previously developed software. Integration testing is designed to assess whether the interfaces between modules (defined below) in a given subsystem have consistent assumptions and communicate correctly. Integration testing must assume that modules work correctly. Some testing literature uses the terms integration testing and system testing interchangeably; in this book, integration testing does not refer to testing the integrated system or subsystem. Integration testing is usually the responsibility of members of the development team.
- 软件开发的子系统设计阶段需要确定子系统的结构和行为,每个子系统都是用来满足整体架构的某些功能。子系统经常是基于已开发软件的应用。
- 集成测试用来检测在子系统中各个模块是否有一致的前提条件并且交互正确。集成测试必须假设各个模块都工作正确。一些测试书籍中集成测试和系统测试表达意思类似,但是本书中,集成测试不是指测试集成系统或者子系统。
- 集成测试经常是开发团队的责任。
模块测试(Module Test)- 细节设计(Detailed Design)
The detailed design phase of software development determines the structure and behavior of individual modules. A program unit, or procedure, is one or more contiguous program statements, with a name that other parts of the software use to call it. Units are called functions in C and C++, procedures or functions in Ada, methods in Java, and subroutines in Fortran. A module is a collection of related units that are assembled in a file, package, or class. This corresponds to a file in C, a package in Ada, and a class in C++ and Java. Module testing is designed to assess individual modules in isolation, including how the component units interact with each other and their associated data structures. Most software development organizations make module testing the responsibility of the programmer.
- 软件开发的细节设计阶段需要确定每个模块的结构和行为。
- 一个项目单元或者程序有一个或者多个相邻的语句(statements),然后还有一个名字(name)以让软件的其他部门可以调用(call)。单元(Units)在C和C++中叫做函数(function),在Ada中叫做procedures or functions,在Java中叫做方法(methods),在Fortran中叫做subroutines。而一个模块(Module)是整个在一个文件(file)、包(package)或者类(class)中的相关单元的集合。其对应C语言中的一个文件,Ada中的一个包,C++和Java中的一个类。
- 模块测试用来在隔离状态下检测每个模块,包括每个组成模块之间的交互和他们相关的数据结构(data structures)。
- 在大多数的软件开发组织,模块测试是开发者的责任。
单元测试(Unit Test) - 实现(Implementation)
Implementation is the phase of software development that actually produces code. Unit testing is designed to assess the units produced by the implementation phase and is the “lowest” level of testing. In some cases, such as when building general-purpose library modules, unit testing is done without knowledge of the encapsulating software application. As with module testing, most software development organizations make unit testing the responsibility of the programmer. It is straightforward to package unit tests together with the corresponding code through the use of tools such as JUnit for Java classes.
- 软件开发的实现阶段就是要实实在在的写代码。
- 单元测试用来检测每个单元,是最底层的测试。在某些情况,创建一般用途的模块,单元测试可以在不了解软件整体应用的前提下执行。
- 和模块测试一样,在大多数的软件开发组织中,单元测试是开发者的责任。通过工具(例如用于Java类的JUnit)将单元测试与相关代码直接打包。
回归测试(regression testing)
Not shown in Figure 1.2 is regression testing, a standard part of the maintenance phase of software development. Regression testing is testing that is done after changes are made to the software, and its purpose is to help ensure that the updated software still possesses the functionality it had before the updates
- 图中没有包含回归测试,他是软件开发的维护阶段的标准部分。
- 回归测试需要在软件发生任何变动后进行,目的是用来帮助保证更新的软件在依然可以执行它更新前的功能。